Greenselect® Phytosome®
Browse all Indena’s documents about products, events, company information and so much more.
Go to sectionPeer-reviewed science on Greenselect® Phytosome®
Hormonal changes during menopause can lead to modified body composition, increased lipid tissue and weight gain, which represent major risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
Recently, a randomized clinical trial carried out on overweight post-menopausal sedentary women evaluated the effect of Greenselect® Phytosome® supplementation on the regulation of lipid tissue function, confirming the positive action of the green tea extract in its formulation.1
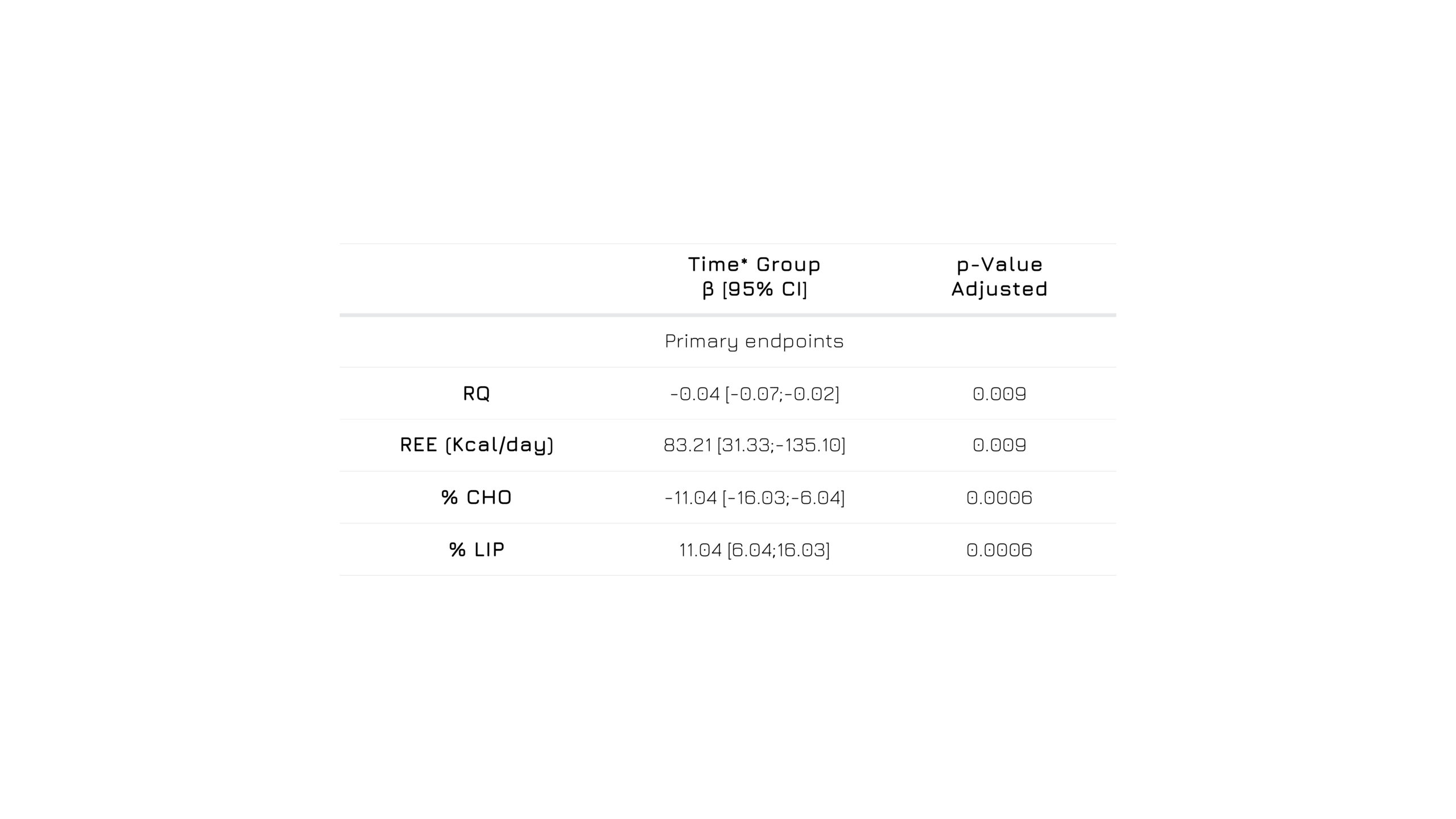
Main indicators of a challenged adipose tissue – such as respiratory quotient (RQ), resting energy expenditure (REE), carbohydrate oxidation (%CHO) and lipid oxidation (%LIP) – were considered and measured at the baseline (t0) and after 30 (t1) and 60 (t2) days of supplementation with 150 mg of Greenselect® Phytosome® or a placebo. To evaluate statistically significant changes over time between the two groups, a coefficient of the interaction between time and group (β,time*group) was estimated. Interestingly, the study showed significant differences over time in RQ (p = 0.009), REE (p = 0.009), %CHO (p = 0.0006), and %LIP (p = 0.0006) levels.1
Figure 1: Pre-and post-supplementation differences between groups for primary endpoint. The table reports the estimates of time* group (β), 95% confidence interval (CI), and adjusted p-value of the null hypothesis of no effect.1
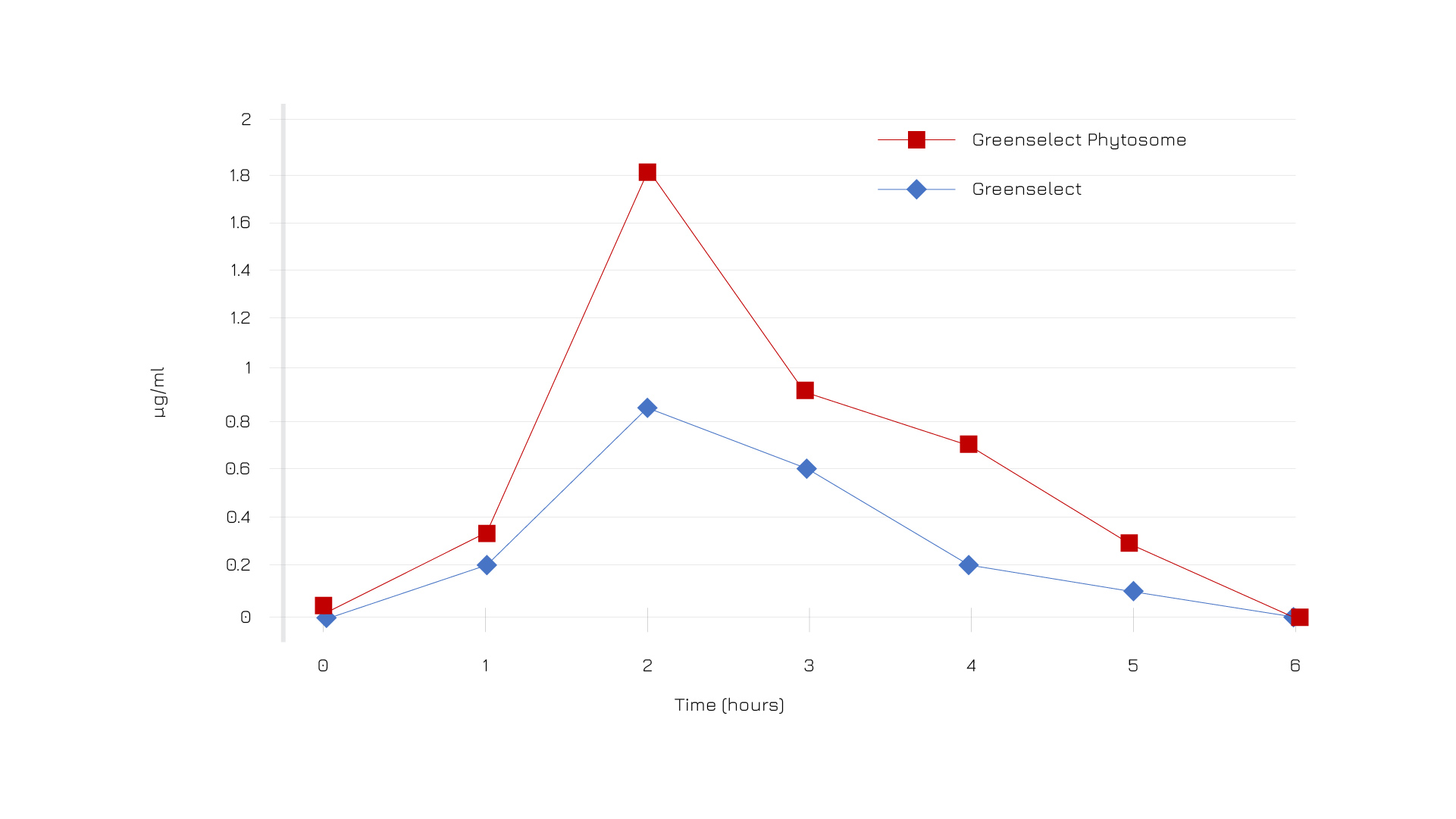
The distinctiveness of Indena’s proprietary delivery system emerges clearly when observing the difference between the plasma concentration profiles of two different catechin extracts, with or without Phytosome®: Greenselect® Phytosome® and Greenselect®.2
Plasma EGCG profiles in healthy subjects were monitored after ingestion of a single dose of one of the two preparations, containing 240 mg of tea catechins each. After 2 hours, the difference in peak concentration was dramatically different: EGCG concentration with Greenselect® Phytosome® was more than doubled and remained higher over time.2
Figure 2: Plasma EGCG profile after ingestion of a single dose of Greenselect® Phytosome® or Greenselect®.2
Different human studies have demonstrated that green tea catechins are coadjutants of a low-calories diet aimed at managing body weight. This positive effect is related to their distinctive ability to act on caloric consumption through increased thermogenesis.
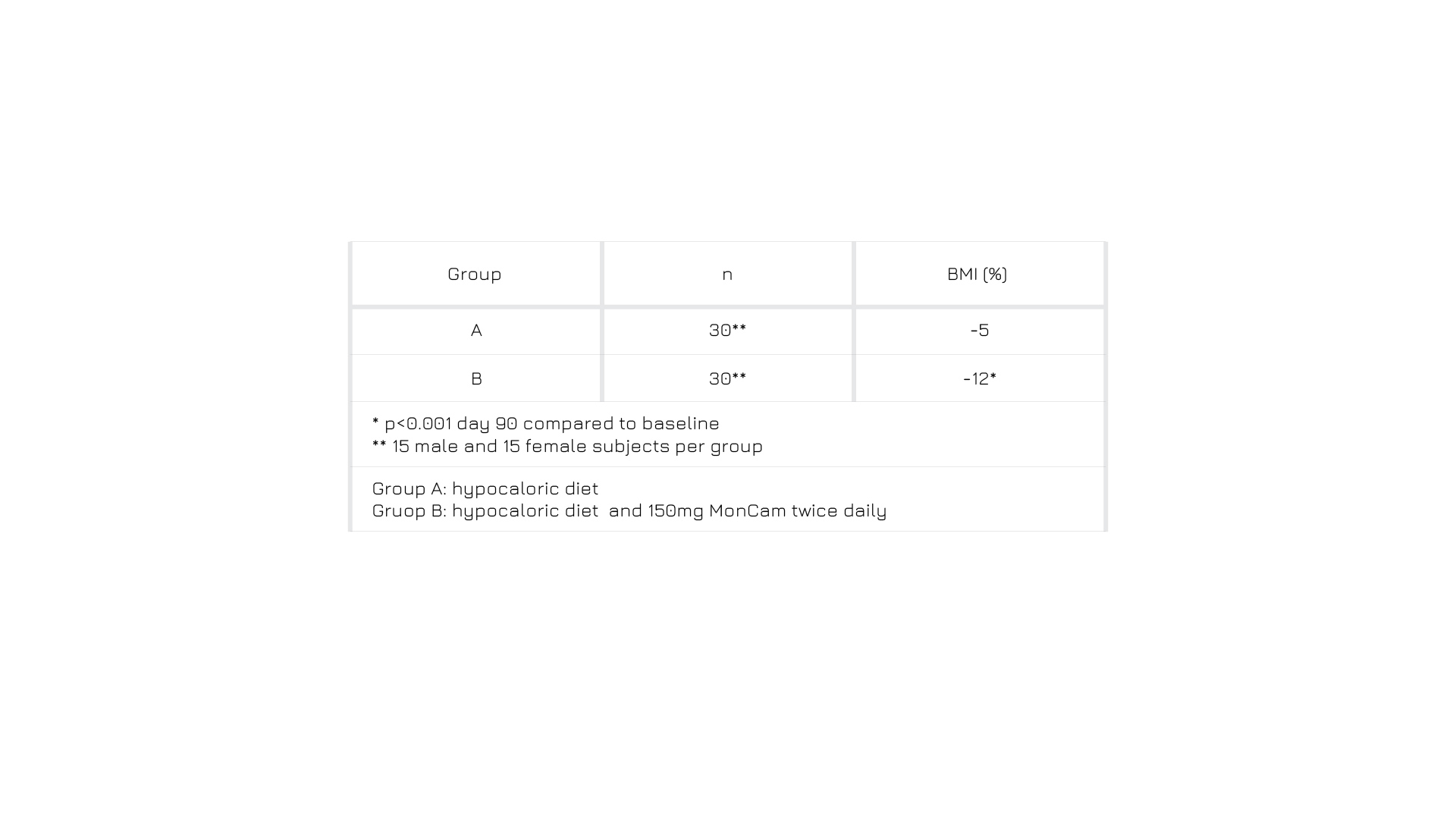
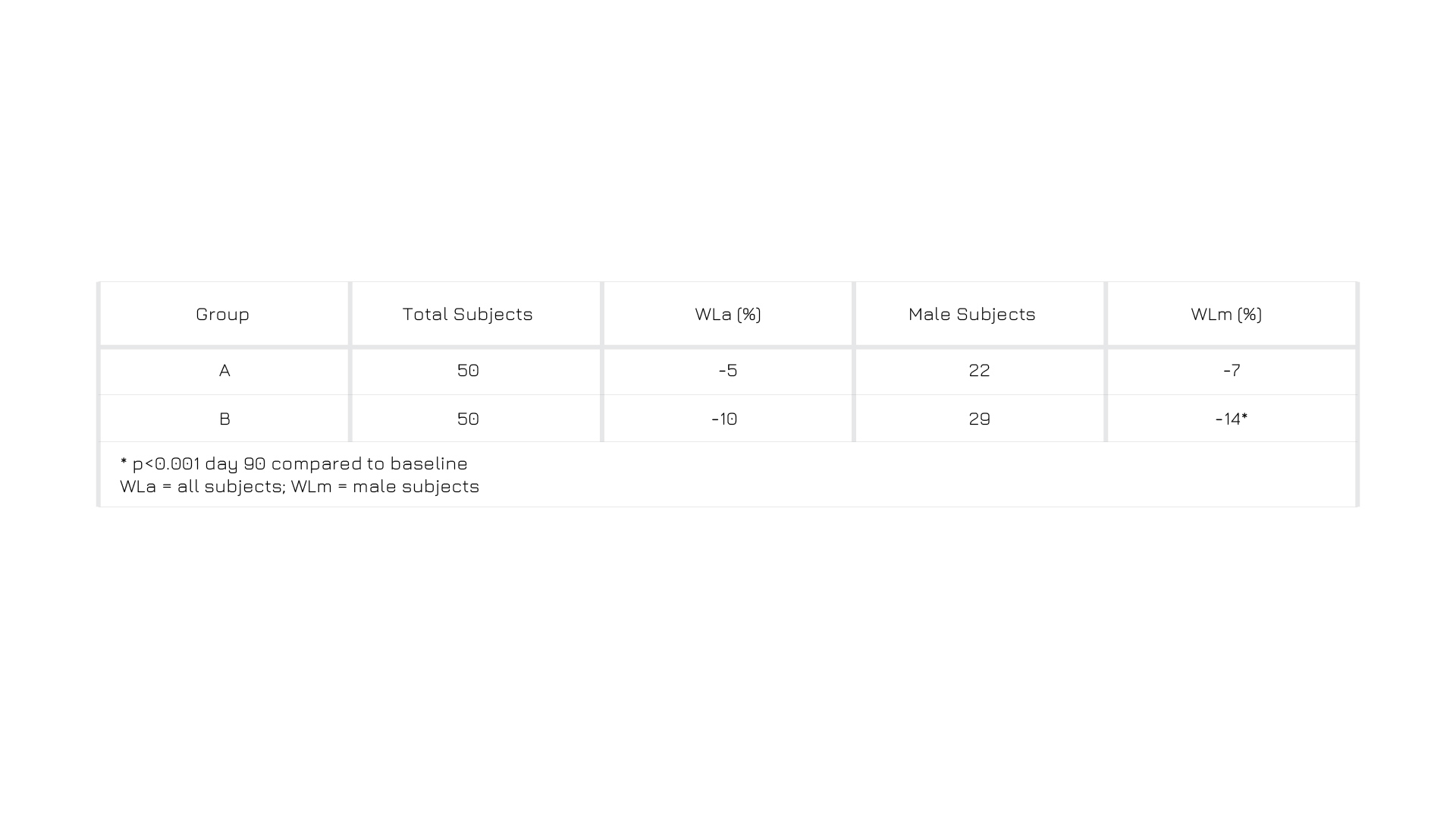
During a period of 90 days, a wide group of overweight participants followed a balanced hypocaloric diet, with or without daily supplementation of Greenselect® Phytosome®. The difference in weight loss was unmistakable: individuals who just restricted calories decreased their BMI by 5% on average, while those also taking Greenselect®Phytosome® reached -12% (p<0.001 on day 90, compared to baseline). Moreover, the difference in average waistline measurements was evident for males, in comparison to their baseline.3
Figure 3: Weight management expressed in terms of BMI modulation in the two groups following a low-calorie diet only (A), or following the same diet and taking a daily dose of tablets containing Greenselect® Phytosome® (B).3
Figure 4: Weight management expressed in terms of waistline measurement difference, in the two groups following a low-calorie diet only (A), or following the same diet and taking a daily dose of tablets containing Greenselect® Phytosome®3 (B).
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Rondanelli M. et al. Nutrients.14(24):5209 (2022).
2. Pietta P. et al., Biochem.Mol. Biol. Intl. 46: 895-903 (1998).
3. Di Pierro F. et al., Alternative Medicine Review.Volume 14, Number 2 (2009).
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.