バズガード®
製品、イベント、会社情報などのインデナの文書を閲覧できます。
セクションに移動バズガード®査読付き科学論文
二重盲検プラセボ対照試験において、バズガード®は健康なボランティアの腹部脂肪を-12%有意に減少させた:
- 有意な結果は1ヵ月以内に観察された
- the optimization of abdominal fat translated into a global improvement of the glycolipidemic profile
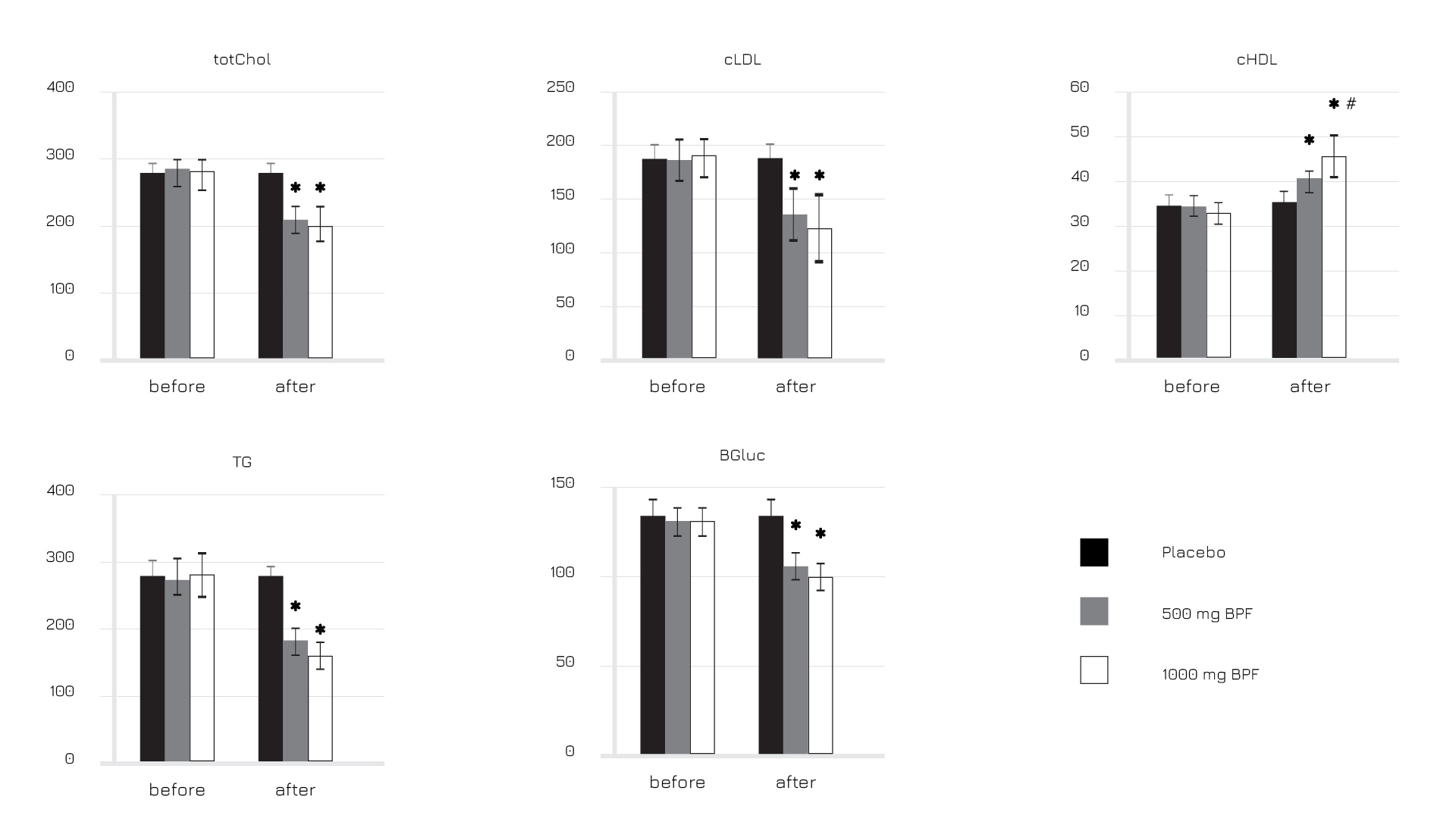
- LDL/HDLコレステロールが有意に最適化された
- リポ蛋白Apo-AおよびApo-Bにも有益な効果が観察された
- 脂質プロファイルの改善は、年齢や性別の点で幅広い集団においても観察された
- 血糖値の中等度の最適化が観察され、インスリン抵抗性パラメータ(HOMA)に対してより顕著な有益な効果が認められたことから、バズガード®の食欲抑制に対するサポートが示唆された。
- トランスアミナーゼに反映される肝機能の正常化もサプリメントによってサポートされた。
バズガード®は、肥満、糖尿病、心血管リスクに関連する腸内細菌叢であるファーミキューテス属とバクテロイデーテス属を減少させる潜在的な有効性を示した。
図1:総コレステロール(totChol)、LDLコレステロール(cLDL)、HDLコレステロール(cHDL)、トリグリセリド(TG)および血糖値(BGluc)に対するベルガモットポリフェノール分画(BPF)の介入前後の効果。
バズガード®は、腹部脂肪、肥満、糖尿病の発生に関与する腸内細菌叢に作用することが実証された。
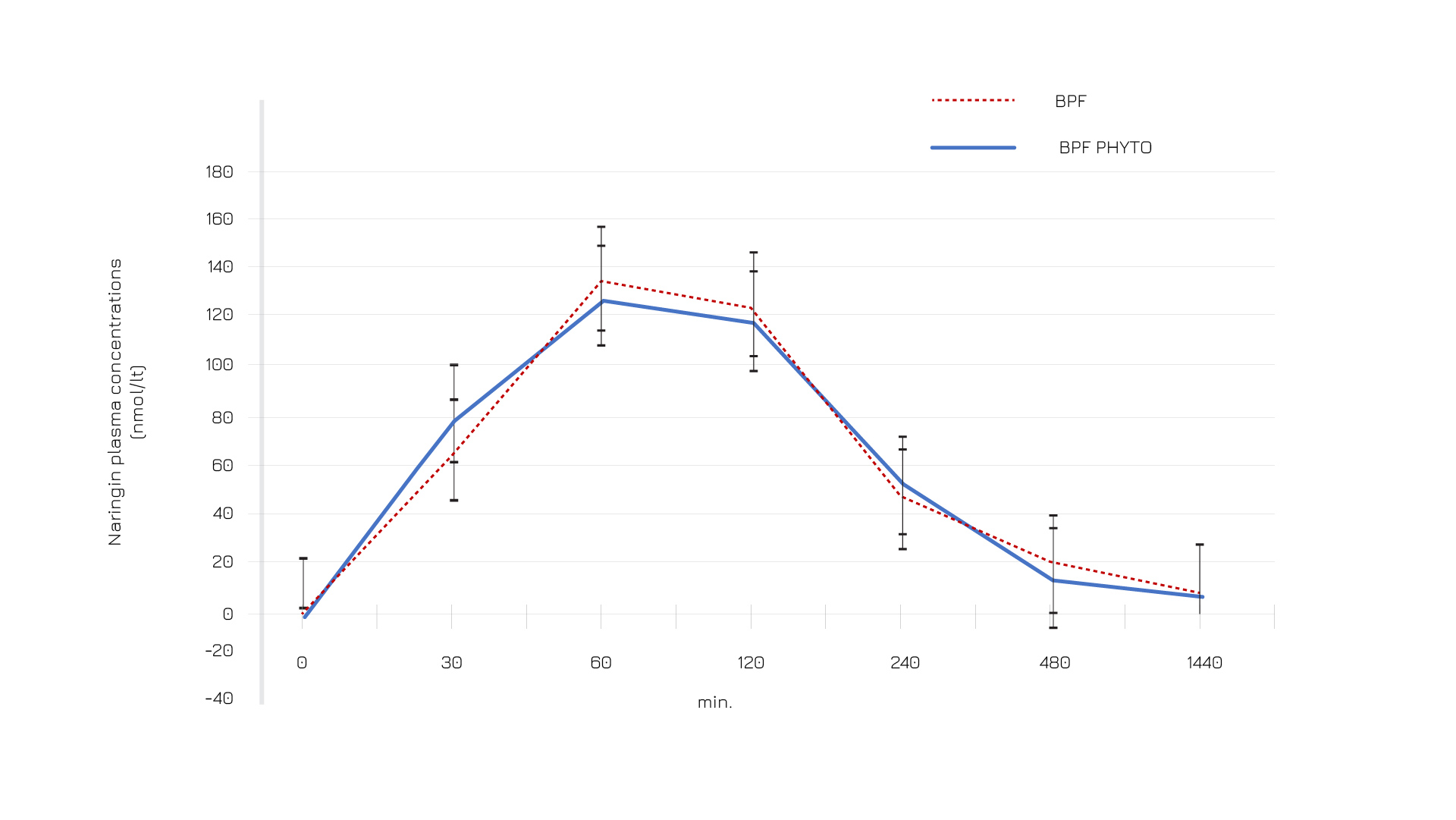
BPFのフィトソーム®製剤は、標準製剤と比較して最適な吸収を示しています。被験者60人を対象に実施したヒト試験(20人にを投与)では、フィトソーム®製剤と比較して、バズガード®の生体吸収が2.5倍増加することが示されています。
フィトソーム®送達システムを使用した場合、cHDLの有益な活用に伴い、空腹時血漿グルコース、血清中cLDLおよびトリグリセリドの有意な平準化も認められています。
図2:標準的なベルガモットポリフェノール分画(BPF)およびベルガモットポリフェノール分画(BPF)フィトソーム®製剤摂取後の血漿中のナリンギンプロファイル。
参考文献
1- Formisano C. et al,J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167;
2- Di Donna L et al J Nat Prod 72:1352–1354 5 (2009)
3- Mollace V. et al.,Endocrine Metabolic& Immune Disorders – Drug Targets 2019, 19, 136-143;
4- Rondanelli M. et al., Phytotherapy Res. 2020, in press;
5- Ramaschi G.,et al, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167
6- Riva A. et al., J Appl.Microb Res. 2020, 3 (2), 45-51.
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.